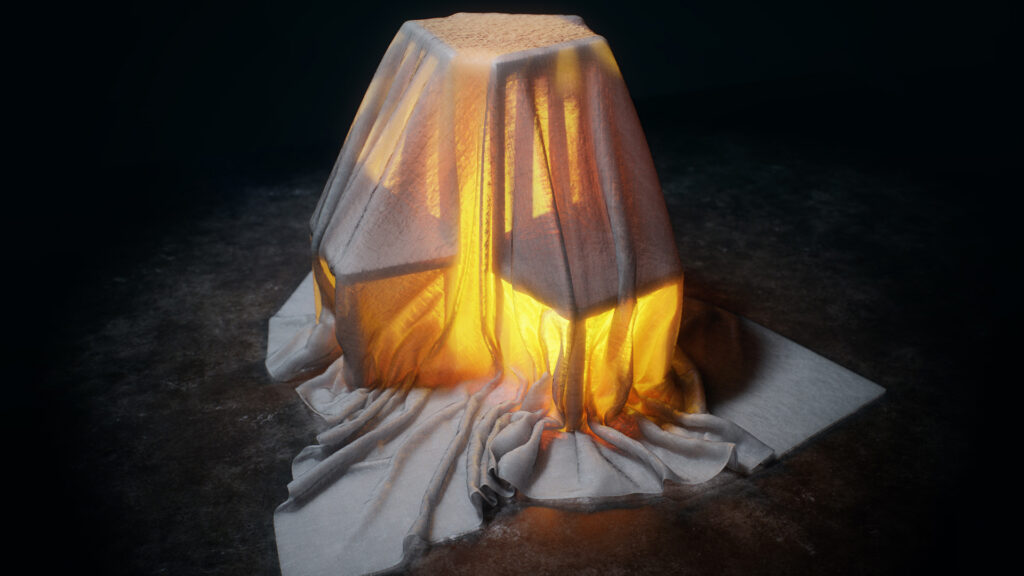
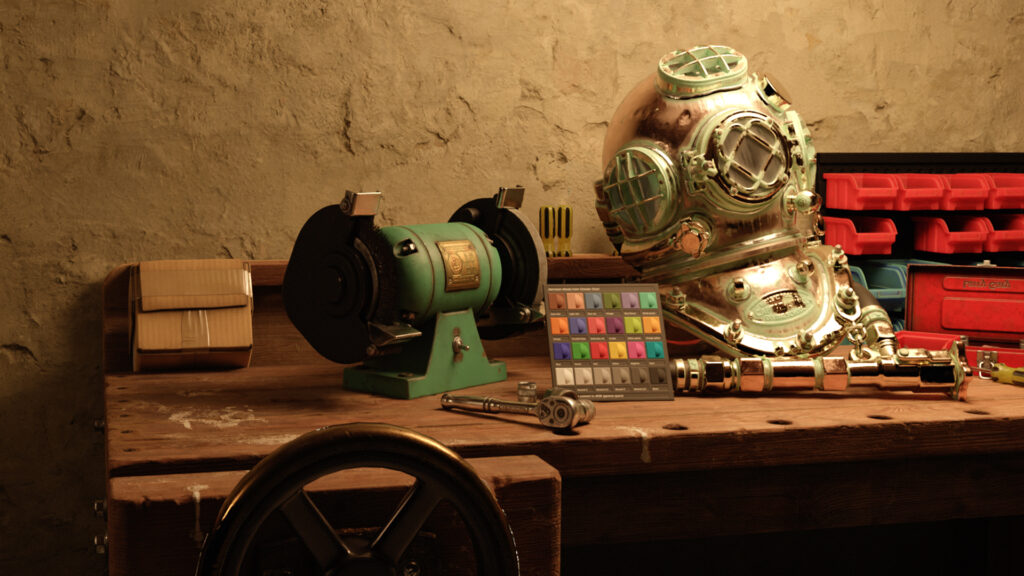
Using Microfiber mode in the Diffusion shader module simulates the appearance of fine natural fibers such as velvet, suede, or upholstery fabric. They produce a soft, realistic surface by modeling how light scatters and reflects along tiny strands. This results in a distinctive, view-dependent sheen that shifts as the camera or lighting changes.
It can use two grayscale maps:
- Sheen Texture Map: Defines the intensity of the microfiber sheen, controlling how strongly the surface reflects light from different viewing angles.
- Sheen Roughness Map: Controls the sharpness of the sheen highlights. Lower roughness produces crisp, well-defined reflections, while higher roughness creates a softer, more diffuse look.
Both texture maps can be sourced from the Toolbag Library, painted directly in a Texture Project, or authored in third-party applications.
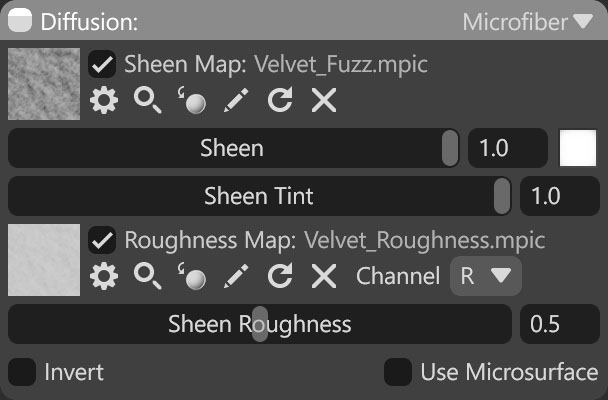
| Setting | Description |
|---|---|
| Sheen Map Texture Slot | Add a sheen texture by clicking on the slot or dragging and dropping one from the Library. |
| Sheen | Adjusts the brightness of the microfiber sheen, a view-dependent reflection effect. |
| Sheen Color | Adjusts the color of the sheen effect. |
| Sheen Tint | Modifies the extent to which sheen color combines with the final effect. |
| Roughness Map Texture Slot | Selects the color channel used in the roughness map. |
| Channel Selection | Determines which channel of the texture map will be used. It’s useful when, instead of using multiple single textures, you use one texture with different grayscale maps in the different texture channels: Red, Green, Blue, and Alpha. |
| Sheen Roughness | Adjusts the microfiber roughness to affect the shape and size of sheen highlights. |
| Invert | Inverts the roughness values, providing the opposite appearance. |
| Use Microsurface | Enables using the material’s primary roughness/gloss value for sheen rendering. |



