Roughness controls a surface’s microsurface irregularity, affecting how blurry or diffuse reflections appear. Higher roughness values create soft, scattered reflections, while lower values produce sharper, more focused reflections. Roughness is effectively the inverse of Gloss.
Use cases include:
- Controlling reflection clarity across metals, plastics, or painted surfaces.
- Adding subtle variation to avoid overly uniform or unrealistic highlights.
Roughness maps can be created in several ways:
- Bake Projects in Toolbag: Generate roughness data from a high-resolution source.
- Toolbag Library: Use pre-made textures.
- Texture Projects in Toolbag: Paint or procedurally generate roughness maps.
- Third-Party Applications: Author maps externally.
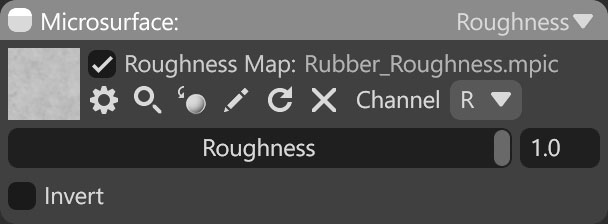
| Setting | Description |
|---|---|
| Roughness Map Texture Slot | Add a roughness texture by clicking on the slot or dragging and dropping one from the Library. |
| Channel Selection | Determines which channel of the texture map will be used. It’s useful when, instead of using multiple single textures, you use one texture with different grayscale maps in the different texture channels: Red, Green, Blue, and Alpha. |
| Roughness Value | Specifies the maximum roughness value. |
| Invert | Inverts the output of the roughness shader. Useful for loading gloss maps in place of roughness maps. |

