The Thin Surface shading model is designed for materials made of delicate, light-transmitting surfaces such as plastic bottles, packaging films, or cellophane. It simulates how light passes through thin geometry to produce realistic translucency effects.
This shading model can use two texture maps:
- Translucency Map (Grayscale): Controls how much light is transmitted through the material. White values allow more light to pass through, while black values block it. Intermediate grays create varying levels of translucency.
- Mask Map (Grayscale): Defines which areas of the material are transparent or opaque. White areas allow light to pass through (affected by the translucency settings), while black areas remain fully opaque.
Both maps can be painted or generated using Toolbag’s Texture Projects, or authored externally in third-party applications.
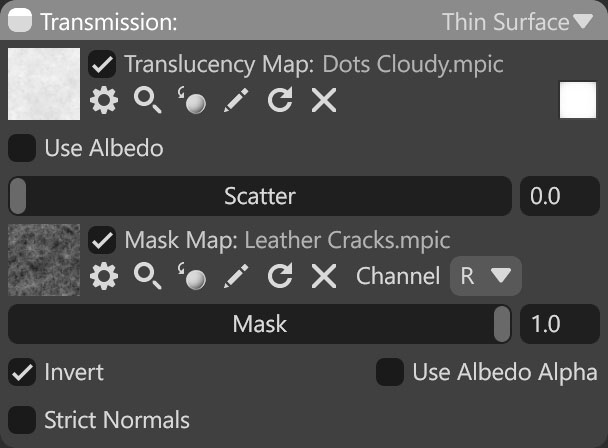
| Setting | Description |
|---|---|
| Translucency Map Texture Slot | Add a translucency texture by clicking on the slot or dragging and dropping one from the Library. |
| Color | Tints the translucency effect. |
| Use Albedo | Use the material’s albedo color for translucency. |
| Scatter | Determines the amount of light scattering inside the surface. |
| Mask Map Texture Slot | Add a translucency mask texture by clicking on the slot or dragging and dropping one from the Library. |
| Mask Value | Sets the mask value that determines the strength of transmission. This value should be set to 1 when a mask map is loaded. |
| Invert | Inverts the mask value so that darker pixels correspond to stronger transmission. |
| Use Albedo Alpha | Uses the material’s albedo alpha value to provide a transmission mask. |
| Strict Normals | Use geometric normal to deciUse geometric normal to decide if a ray points towards inside or outside of the mesh. Enabling this option might help with light leaks on low poly or poorly tessellated meshes. Applies only to ray tracing. |

